Table of Contents
Overview | Hypothyroidism | Hyperthyroidism | Natural Support | Q&A
Summary:
"A thyroid problem in a dog is usually due to a decrease or increase in the production of thyroid hormone. A decrease is referred to as hypothyroidism, while an increase is referred to as hyperthyroidism.
Hypothyroidism is thought to be genetic while hyperthyroidism is commonly caused by a thyroid tumor (carcinoma). Hyperthyroidism is extremely uncommon in dogs. Treatment for involves the removal of the diseased sections of the thyroid in hypothyroidism and synthetic hormone replacement therapy where needed in both forms of thyroid disease.
Hypothyroidism can be easily controlled with an excellent prognosis. The prognosis for hyperthyroidism depends on the size of the thyroid tumor and if the cancer has spread. Holistic veterinarians believe natural medicine can be used to stimulate hormone production. All treatment recommendations are based on the exact condition of your dog's thyroid."

Source: European Society of Veterinary Dermatology
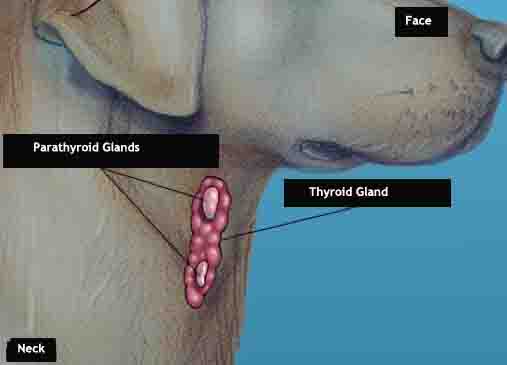
Overview
The thyroid gland is found in the neck and is made up of two lobes. This gland regulates the speed at which other body processes work. The thyroid gland is part of a three gland system including the hypothalamus and the pituitary. Problems in either of these glands can negatively impact the amount of hormone released by the thyroid. Diseases such as Hypothyroidism (too little hormone) and hyperthyroidism (too much) are a direct result of this gland system not operating properly.
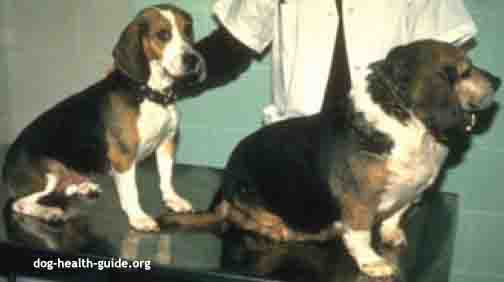
Dog Hypothyroidism
Dogs with this condition are suffering from the a tumor destroying the thyroid or the pituitary gland. Since hypothyroidism in dogs is related to less hormone, this directly relates to a slowing down of body systems. Specifically this means that there is a drop in production of thyroxine (T4) and 3,5,3 triiodothyronine (T3). One in 250 dogs develop the condition. The mean age is 7 years old.
Source: Oxford Labs
The disorder is referred to as being primary (caused by a problem in
the thyroid gland, in a form called lymphocytic thyroiditis and
Idiopathic thyroid atrophy), secondary (caused by another process in
the dog such as a pituitary gland problem), or tertiary (caused by the
part of the brain called the hypothalamus).
Hyperadrenocorticism and diabetes mellitus have been linked to the disease.(2)
Causes
- Lymphocytic thyroiditis: When the thyroid is infiltrated by
lymphocytes, which are small white blood cells that help the immune
system function
- Idiopathic thyroid atrophy: Where the thyroid gland wastes away
with no known cause
- Neoplasia: Cancerous tumor growth
- Pituitary
Disease: Abnormal pituitary function
- Congenital problems
- Iodine deficiency due to dietary problems
- Iatrogenic: caused by a surgical procedure or radiation therapy
Breeds
Large breed dogs have a higher incidence of hypothyroidism:
- Doberman Pinscher
- Golden Retriever
- Labrador Retriever
- Cocker Spaniel
- German Shepherd dog
- Dachshund
- Poodle
- Rottweiler
- Spaniels
- Terriers
- Boxer
- Mixed breeds
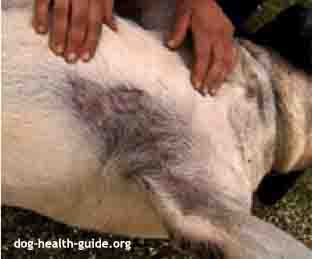
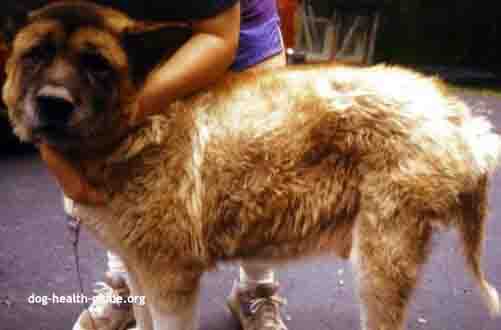
Dog Thyroid Symptoms
The behavioral, gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, nervous, neuromuscular, ocular (eyes), skin and reproductive systems can be affected. Typical symptoms are:
- hair loss
- weight gain
- lethargy
Other Symptoms:
- mental dullness
- decrease in activity
- weakness
- can't keep warm
- dry skin
- shedding
- dry or dull coat
- seborrhea
- skin infection/skin pus
- ear canal infection (otitis externa)
- skin thickening and puffy eyes (rare)
Rare Symptoms:
- Facial paralysis
- Conjunctivitis
Symptoms are similar to euthyroid sick syndrome (normal thyroid function accompanied by abnormalities in the level of hormones in the body, usually seen in sick patients), which needs to be differentiated by hypothyroidism before a final diagnosis can be made.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis for this type of dog thyroid problem involves measuring the amount of thyroid hormone being produced.
Treatment
Thyroid problem in dog treatment due to hypothyroidism involves replacement therapy of the hormone for the life of the patient. It may take some experimentation by your veterinarian to get the level right. Dogs will have a normal lifespan after treatment and any symptoms should clear. Dogs will be tested for thyroid function 6 weeks after starting therapy, then every 6 to 8 weeks for 6 to 8 months, then 2x per year.
If the condition is left untreated dogs can develop myxedema (skin swelling), myxedema coma or atherosclerosis (build up of plaque in the blood vessels).
Dog Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism means that your dog is producing too much thyroid hormone. There is a higher incidence of the disease in Labrador Retrievers. The condition is usually caused by a dog thyroid tumor and is a very aggressive form of cancer, with 10% of dogs with a thyroid carnicoma being hyperthyroid (1). A form of hyperthyroidism in dogs, Iatrogenic hyperthyroidism is caused by over supplementation, but is rare.
Symptoms
This excess hormone causes the metabolism to speed up resulting in:
- weight loss
- desire to eat more
- faster heart rate
- increased urination
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- shortness of breath
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made by measuring the levels of thyroid hormone in your dog's body.
Treatment
Treatment of hyperthyroidism involves surgically removing the diseased portion of the thyroid and then using hormone replacement therapy if needed. Chemotherapy, radioactive iodine therapy are also used depending on the tumor size, how invasive it is in surrounding tissue and if it has started to metastasize or spread to other organs.
Natural Medicine
Holistic veterinarians believe that in the case of hypothyroidism, that natural medicine (herbal remedies) can be used to naturally stimulate hormone production vs. the man made synthetic kind prescribed be veterinarians. It might be worth discussing with your veterinarian alternatives such as the one made by Pet Alive called Thyro-Pet.
Ask a Question or Share a Story
Have A Question About Hypothyroidsim or Story That Can Help Others?
Do you have a Canine Hypothyroidism related Question for our Editors or a Helpful Story to Share? Please include information such as age, sex, breed, medical history, skin and other symptoms, medications your dog is taking, recent changes in behavior, etc. A picture of the condition would also be helpful.
We will do our best to get back to you quickly (depends on how many questions we receive each day). If you do require an immediate response we suggest using this online dog veterinary service that is available now.
References:
(1) Feldman EC, Nelson RW. Canine thyroid tumors and
hyperthyroidism. In: Feldman EC, Nelson RW. Canine and Feline
Endocrinology and Reproduction. St. Louis: WB Saunders, 2004, pp
219-249.
(2) Feldman EC, Nelson RW. Hypothyroidism. In: Feldman
EC, Nelson RW. Canine and Feline Endocrinology and Reproduction. St.
Louis: WB Saunders; 2004, pp 86-151.
Merck/Merial Manual for Pet Health
Canine Hypothyroidism
Shomom, Mary
The Mechanic's Guide to Your Patient's "Idle System": Thyroid
Disease Reviewed
K.K. Faunt
The Pet Hospital, Portland, OR, USA.
